
You could also make bulk code updates in few clicks irrespective of the number of directories and files. Using GitHub Desktop client, you can easily manage the codes locally. Authenticate GitHub to push the changesġ5. Click on “Save and retry” to push the changes to git repository. You need to pass the valid credentials to authenticate the repo. Click on “ Commit to Master” Commit to Master branchġ3. Add meaningful comments to commit the changes. You could also copy directories and files to that path to upload to GitHub repository. It will automatically detect the code changes. Let’s make some changes on the README.MD file to test. Click on “Show in explorer” to see the files and folders on the repo. It just displays that, we haven’t made any local changes so far.

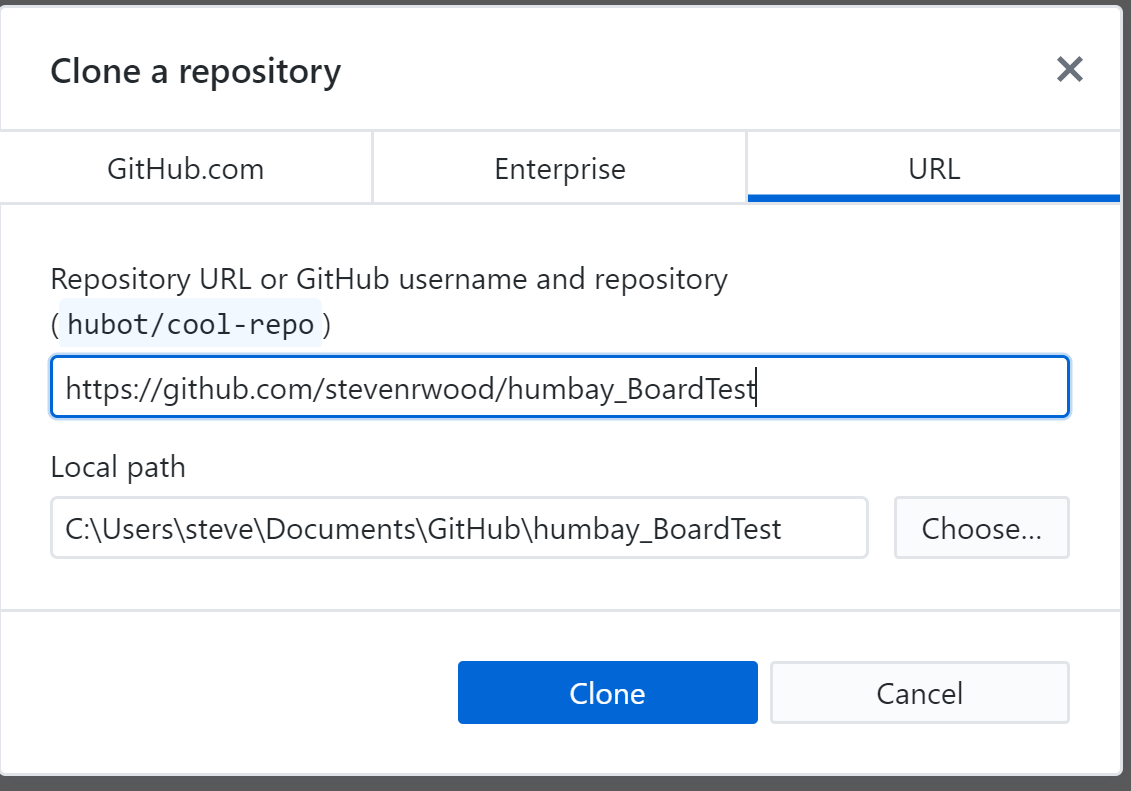
Once the repository is cloned, you could see the following screen. Click on clone to pull the repository to local path. Enter the copied repo URL and select the local directory path. Paste the copied link in the URL or username/repository bar. In Desktop GitHub, click on “Clone a repository from the Internet” Desktop GitHub – Clone RepoĨ. Now, go back to the Github Desktop window.
Copy the GitHub repository URL from webpage. You could also opt out sending periodic usage statistics to GitHub. Click Finish complete the local configuration. Just enter your name and email address to configure locally GitHub Desktop – Configure Gitĥ. I have selected “skip to continue” to manually manage the repository. You could also directly logging in to existing GitHub account to manage the repository. Once the GitHub is installed, you will get the welcome page like below.
#Github clone repository to desktop install#
Click on the downloaded executable to install it. You could also upload the codes directly using GitHub web-GUIġ. The desktop client can be installed with normal user privileges. Desktop GitHub Client is one of the tools which can be used to manage the code from your laptop/desktop effectively. GitHub continuously offers many tools to manage the codes effectively. For more information, see " Troubleshooting cloning errors.GitHub is a web-based version control platform to manage the codes. The default branch you want to clone still exists.For more information, see " Troubleshooting cloning errors." You have permission to access the repository you want to clone.We will use the git init command to initialize. For more information, see " Troubleshooting cloning errors." Let us first create a Git repository using Git Bash or Visual Studio or a similar command line that supports Git. If you're unable to clone a repository, check that: When cloning a repository it's possible that you might encounter some errors. > remove: Total 10 (delta 1), reused 10 (delta 1) > Unpacking objects: 100% (10/10), done. > remote: Compressing objects: 100% (8/8), done. $ git clone > Cloning into `Spoon-Knife`. Type git clone, and then paste the URL you copied earlier. Īlternatively, to clone your repository in Desktop, click Set up in Desktop and follow the prompts to complete the clone.Ĭhange the current working directory to the location where you want the cloned directory. To clone the repository using an SSH key, including a certificate issued by your organization's SSH certificate authority, click SSH, then click. To clone your repository using the command line using HTTPS, under "Quick setup", click. It's often made if you don't initialize the repository with a README when creating it. To clone and open the repository with GitHub Desktop, click Open with GitHub Desktop.įollow the prompts in GitHub Desktop to complete the clone.įor more information, see " Cloning a repository from GitHub to GitHub Desktop." Cloning an empty repositoryĪn empty repository contains no files.
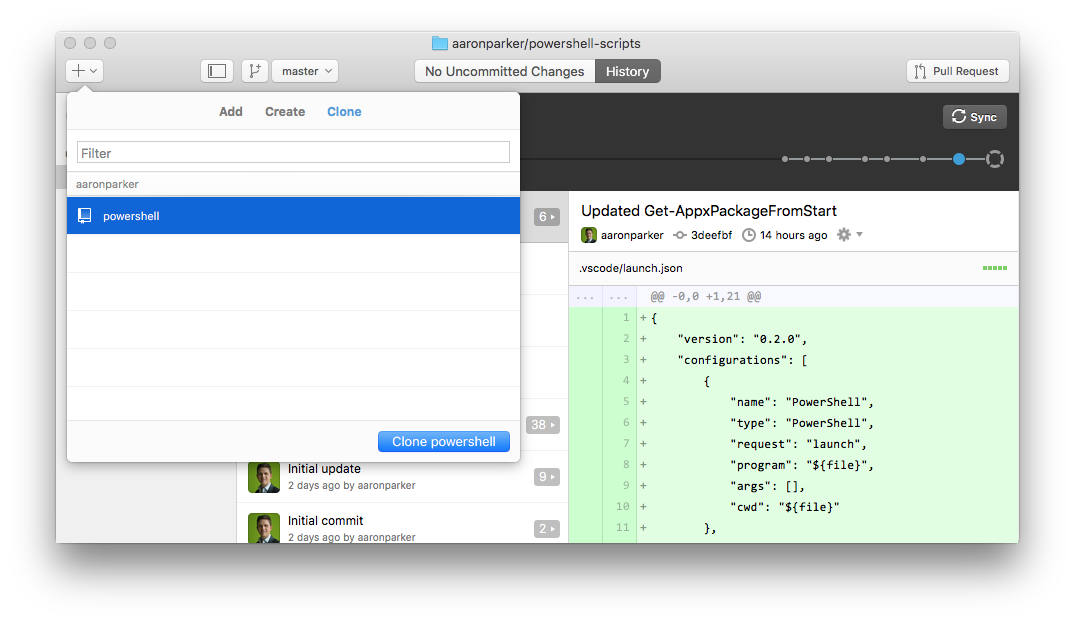
On, navigate to the main page of the repository.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
